
In the world of modern communication, the importance of high-frequency connectors cannot be overstated. John Smith, a leading expert in the field, stated, "High-frequency connectors are essential for reliable data transmission." As technology advances, these connectors ensure high-speed performance. They allow devices to transmit signals without degradation.
High-frequency connectors play a key role in various industries. They are found in telecommunications, aerospace, and even automotive applications. Each of these areas demands precision and reliability. As systems evolve, the need for robust connectors grows more significant. Mistakes can cost companies time and money, highlighting the urgency for innovation and improvement.
Understanding high-frequency connectors is crucial for engineers. They face challenges in maintaining signal integrity while minimizing interference. The continuing development of these connectors reflects the industry's need for better performance. Ongoing research is vital, as the landscape changes rapidly.

High frequency connectors are vital components in many electronic systems. They are designed to transmit signals at high frequencies, often exceeding 1 GHz. These connectors play a significant role in applications such as telecommunications, satellite communications, and high-speed data transfer.
The main characteristic of high frequency connectors is their ability to maintain signal integrity. This integrity prevents signal loss, reflection, or interference. Many designs utilize specific materials and construction techniques to reduce these unwanted effects. A poorly designed connector can lead to poor performance and unreliable connections. Precision in manufacturing is crucial, yet not all connectors meet the demanding specifications.
Different types exist, and each serves unique purposes. Some connectors are well-suited for coaxial cables, while others cater to different connectivity needs. Despite their advantages, the market can be overwhelming. Many users might find it challenging to select the right connector. Making an informed choice requires a clear understanding of the specific application and system requirements. Often, trial and error become part of the selection process.
| Connector Type | Frequency Range | Impedance | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA Connector | 0 to 18 GHz | 50 Ohm | RF Applications, Telecommunications | Compact size, screw coupling, excellent electrical performance |
| SMB Connector | 0 to 4 GHz | 75 Ohm | TV and Cable applications | Snap-on coupling, small size, good electrical characteristics |
| N Connector | 0 to 11 GHz | 50 Ohm | Broadcast, outdoor RF applications | Robust design, weatherproof, reliable |
| BNC Connector | 0 to 4 GHz | 75 Ohm | Video, RF communications | Easy to connect/disconnect, good performance |
| TNC Connector | 0 to 11 GHz | 50 Ohm | Radio, wireless communications | Threaded coupling, strong connection |
High frequency connectors are vital in various industries. They help manage signals in telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive sectors. Each application requires unique specifications. These connectors ensure reliability and performance in high-speed environments.
There are several types of high frequency connectors, such as SMA, N, and BNC. For instance, SMA connectors are widely used in microwave applications. They offer a frequency range up to 18 GHz. Meanwhile, the N connector is suitable for connections in networks, dealing with frequencies up to 11 GHz. BNC connectors are popular for video transmissions. They operate efficiently in a frequency range of 4 GHz.
The choice of connector impacts the overall system performance. A report indicates that the global market for high frequency connectors is projected to grow significantly. By 2025, the demand may reach billions of dollars. This growth reflects the increasing need for high-speed data transmission. However, challenges persist regarding compatibility and manufacturing precision. These issues require careful consideration in design and maintenance.
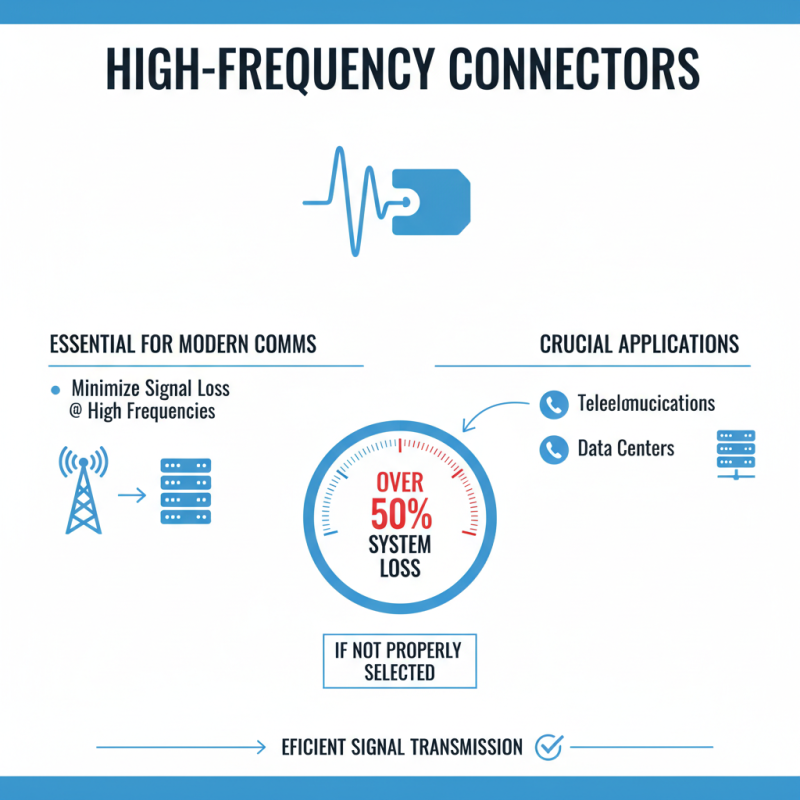
High frequency connectors are essential for modern communication systems. They operate on the principle of minimizing signal loss at high frequencies. These connectors are designed to transmit signals efficiently, which is crucial for applications in telecommunications and data centers. According to industry reports, connectors can contribute to over 50% of the total system loss if not properly selected.
Understanding the principles of operation is vital. High frequency connectors use advanced materials and geometric designs to manage impedance. This helps in maintaining signal integrity. The characteristic impedance typically ranges from 50 to 75 ohms. Variations in this can lead to reflections, causing performance issues.
Tips: Always consider the installation environment. Factors like temperature and mechanical stress can affect performance. Proper handling is also crucial. A poorly installed connector can lead to unexpected failures. Regular testing can identify issues before they escalate. Overall, while connectors seem simple, their impact on a system is profound.
High frequency connectors play a vital role in modern electronics. They are essential for high-speed data transmission. These connectors are designed to minimize signal loss. This is particularly important for applications like telecommunications and data centers.
Key performance characteristics include impedance stability. Maintaining a consistent impedance ensures signals reach their destination without distortion. Additionally, high frequency connectors must exhibit low insertion loss. This allows for clearer signals over longer distances. Connectors also need excellent return loss. Poor return loss can reflect signals back, causing interference.
Durability is another crucial factor. Connectors face wear and tear in frequent use. Some designs are prone to failure under stress. Regular testing for performance can help identify these issues. It’s important to review specifications before choosing connectors. Performance can vary widely across different designs. The right choice can greatly enhance system efficiency.
This chart illustrates the key performance characteristics of high frequency connectors, emphasizing factors such as insertion loss, return loss, and VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio).
High frequency connectors face significant challenges as technology advances.
These connectors are essential for applications like telecommunications and aerospace.
The demand for high bandwidth and
low signal loss is crucial.
A recent industry report indicated that the market for high frequency connectors is expected
to grow by 7% annually. This growth emphasizes the
urgent need for innovation.
Manufacturers are exploring new materials and designs. For instance, the use of
ceramic insulators
can improve performance. Yet, integrating these materials into existing processes is not
straightforward. Many companies struggle with compatibility issues. Additionally, the rising
complexity of electronic devices adds to the challenge. Engineers often encounter limitations
in the current designs. This leads to frequent revisions and testing cycles.
Another area of concern is environmental impact. As manufacturers innovate,
sustainability must remain a priority.
Current connector designs often overlook eco-friendly materials. While there is a push
towards green technologies, implementation remains slow. The industry must balance
performance demands with those of environmental stewardship.
Only then can it achieve meaningful progress in high frequency connector technology.






