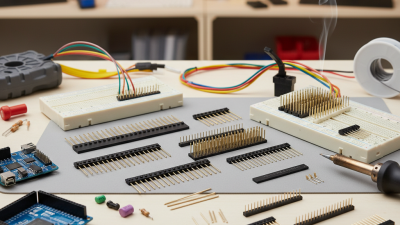

When embarking on electronics projects, one of the most crucial components to consider is the 4 Pin Header Socket. This seemingly simple connector plays a significant role in ensuring that different parts of a circuit communicate effectively. As the backbone of many electronic connections, the right choice of a 4 Pin Header Socket can enhance the reliability and functionality of your project. Whether you are a novice hobbyist or an experienced engineer, understanding the various types, specifications, and applications of 4 Pin Header Sockets is vital for achieving optimal results.
In this guide, we will delve into the essential considerations when selecting a 4 Pin Header Socket for your electronics projects. Factors such as size, pitch, mounting type, and the specific requirements of your project will be discussed to help you make informed choices. By focusing on these key aspects, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to select the most suitable 4 Pin Header Socket that aligns with your project's needs, ensuring robust performance and ease of use. Ultimately, the right socket not only simplifies the assembly process but also contributes to the longevity and effectiveness of your electronic designs.

When embarking on electronics projects, selecting the appropriate 4 pin header socket is crucial for ensuring reliable connections and facilitating efficient circuit design. A 4 pin header socket is a common component in a variety of electronic devices, serving as a modular connection point for attaching wires or other components. Understanding the basic characteristics of a 4 pin header socket—such as pitch, wire gauge compatibility, and material—is essential for making informed choices. Industry reports indicate that a significant percentage of electronic failure rates can be traced back to poor connectivity, emphasizing the importance of high-quality header sockets in project reliability.
The pitch of the header socket, which typically ranges from 2.54mm (0.1 inch) to 1.27mm (0.05 inch), determines the spacing between pins and influences the overall design layout. Moreover, the current rating of the header—reported to affect thermal conductivity and electrical performance—should align with the specific needs of your project. According to research from the Electronics Components Industry Association (ECIA), nearly 30% of electronic design engineers consider the header's thermal characteristics as a key factor in their selection process. Thus, choosing a socket that effectively manages heat can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of your overall system.
Additionally, materials used in the construction of 4 pin header sockets, such as polyamide or thermoplastic, can impact durability and environmental resistance. A study by IEEE found that connectors made from high-grade materials can reduce the incidence of corrosion and wear, improving connection longevity. As such, taking the time to understand the specifications and performance metrics associated with 4 pin header sockets not only aids in project success but also contributes to the long-term viability of electronic designs.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Pin Configuration | 4 pins for power and data connections |
| Pin Spacing | Standard 2.54 mm (0.1 inch) spacing |
| Header Type | Male or Female header |
| Material | Plastic housing with gold-plated contacts |
| Current Rating | Typically up to 3A per pin |
| Usage | Commonly used in microcontrollers and sensors |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 85°C |
| Mounting Type | Through-hole or surface mount options |
When selecting a 4 pin header socket for your electronics project, it is crucial to identify the key specifications that align with your project needs. One primary consideration is the pin spacing, typically measured in millimeters or inches. The most common spacing is 2.54mm (0.1 inches), which is compatible with standard breadboards and perfboards. Ensuring that the spacing matches your board layout will facilitate seamless connections and minimize the risk of short circuits or loose connections.
Another important specification is the current and voltage rating of the header socket. Different projects may require varying electrical specifications; thus, it's essential to choose sockets that can handle the intended load. Exceeding the ratings can lead to overheating and failure of the components. Additionally, consider the material of the socket. Typically, headers are made from durable materials that resist corrosion and wear, ensuring longevity in your electronic setup. By thoroughly evaluating these key specifications, you can select the most suitable 4 pin header socket for your project, enhancing both performance and reliability.
This chart illustrates the current usage in milliamps (mA) for different types of 4 pin header sockets commonly used in electronics projects, helping you make an informed choice based on your project's needs.

When selecting the right 4 pin header socket for your electronics projects, it is crucial to consider the various types available to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Standard, double row, and angled 4 pin header sockets each serve specific applications, catering to differing space constraints and ease of access. According to a recent industry report, the demand for precision connector solutions is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2025, indicating a strong preference for connectors that meet specific form factors and functionality.
Standard 4 pin header sockets, commonly used in prototyping, offer straightforward configurations that suit a wide range of devices. In contrast, double row sockets allow for more robust connections and can accommodate greater pin counts without increasing the physical footprint. This is especially essential in compact electronic devices where space is limited. Meanwhile, angled 4 pin header sockets facilitate easier insertion and accessibility, making them ideal for applications where the orientation of the connection is critical. The choice between these types can significantly impact not only the performance but also the longevity of electronic devices, emphasizing the importance of selecting the correct type for your specific project needs.
Furthermore, thermal and electrical characteristics also play a critical role in selecting the appropriate socket type. Data indicates that improperly chosen header sockets can lead to increased failure rates in electronic circuits, with estimates suggesting that connector-related issues account for nearly 30% of all field failures in electronic equipment. Thus, thorough analysis and testing of the various types of 4 pin header sockets, based on the requirements of your particular application, is essential to ensure reliability and efficiency in your electronic projects.

When selecting the right 4 pin header socket for electronics projects, evaluating quality and durability is paramount. In recent industry reports, it has been highlighted that reliability in connection significantly influences the lifespan of electronic components, with poor-quality sockets being a leading cause of device failure. According to a 2022 study by the Electronic Components Industry Association (ECIA), over 30% of electronic failures in field applications can be traced back to inferior interconnects, emphasizing the need for thorough assessment before making a purchase.
Durability comes from materials used and construction techniques. Sockets crafted with high-grade materials like thermoplastics and featuring gold-plated contacts demonstrate improved corrosion resistance and mechanical longevity. Research from the International Journal of Electronics Manufacturing suggests that high-quality sockets can last up to twice as long in high-stress environments compared to standard alternatives. Therefore, focusing on specifications such as temperature tolerance, contact resistance, and mechanical ratings will ensure your projects maintain performance and reliability over extended use, ultimately saving costs in the long run.
When working with 4 pin header sockets in your electronics projects, proper installation and connection techniques are crucial for ensuring reliable performance. To start with, it's essential to check the orientation of the header and socket before making any connections. Most 4 pin headers have a notch or keying feature that indicates the correct alignment. Mismatched connections can lead to malfunction or damage to components.
One effective tip for ensuring a solid connection is to use a soldering iron with the right size tip for the pins you're working with. A tip that is too large may cause excessive heat exposure to adjacent components, while a tip that is too small will make it difficult to apply sufficient solder to form a lasting joint. Always apply solder to the joint quickly to avoid overheating the pins and potential deformation.
Another important aspect of installation is the use of heat shrink tubing or electrical tape to insulate exposed connections. This not only helps to prevent short circuits but also protects the solder joints from mechanical stress. Additionally, when connecting wires, ensure that the insulation does not come into contact with the header pins to maintain reliable electrical connectivity. By following these tips, you can achieve a more robust and efficient connection in your projects.